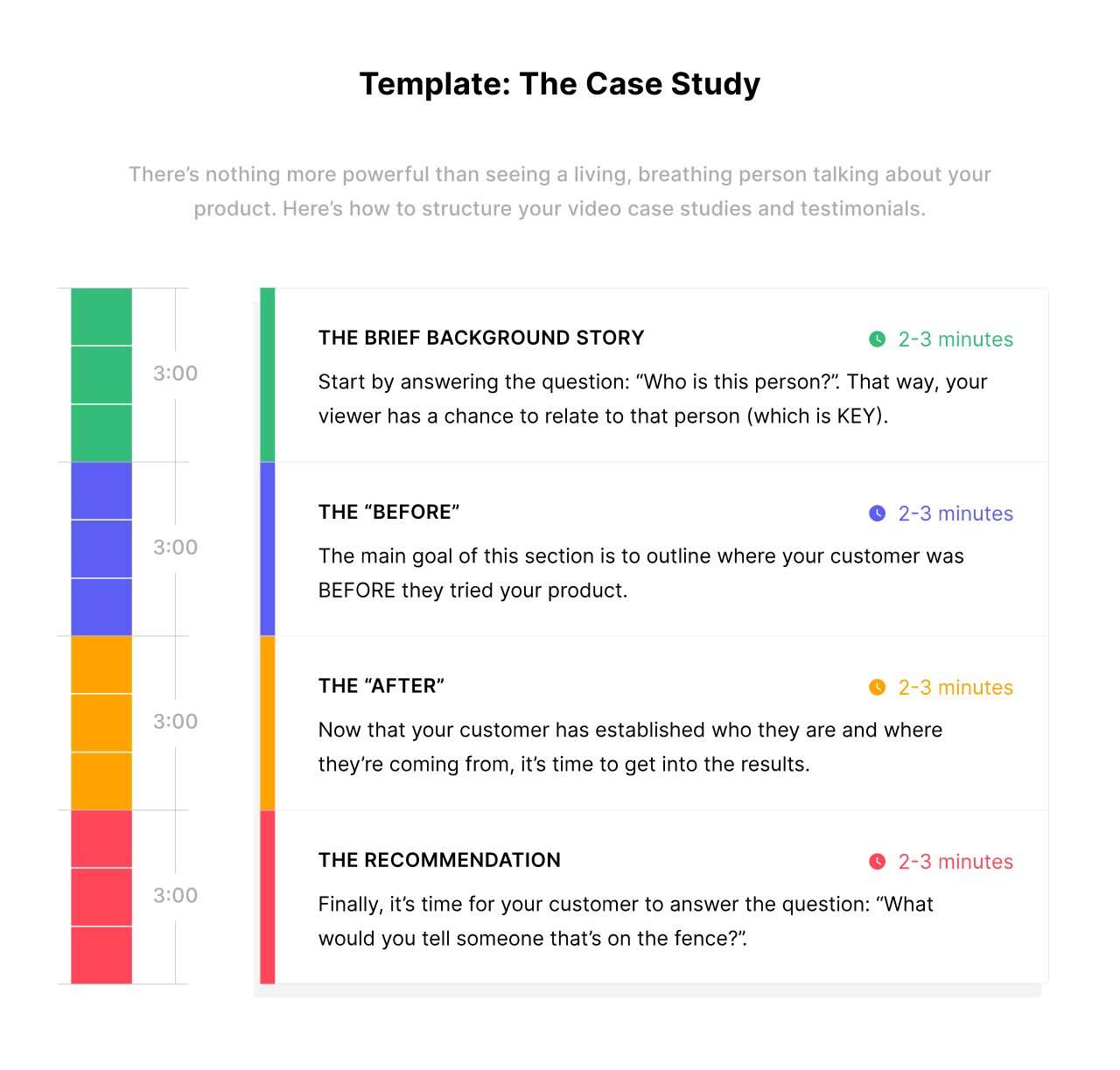
Maximize your website’s SEO potential by integrating essential HTML best practices, from structured data to secure protocols. In digital marketing, SEO is key for boosting website visibility and organic traffic. Central to SEO is HTML, the core language for web content creation. It’s critical for search engines to crawl, index, and rank web pages effectively. Key HTML tags, such as titles, headers, and meta descriptions, communicate web content’s relevance to search engines, impacting user engagement and click-through rates.
Well-structured HTML not only aids search engines in knowing web content but also increase user experience. Websites with logical organization, responsive design, and clear navigation perform better in search rankings and user retention. Advanced HTML elements like schema markup enrich search result presentations, boosting engagement, while HTTPS implementation, indicated in HTML, secures user data and contributes to search ranking signals.
The role of HTML in SEO is foundational, emphasizing the need for web developers and SEO professionals to keep up with best practices and trends. The post will explore specific HTML strategies critical for optimizing websites for search engines and users.
Key Takeaways
-
- Utilize Schema.org for enhanced snippets.
- Ensure mobile responsiveness.
- Optimize speed and images.
- Implement canonical tags for unique content.
- Secure your site with HTTPS.
- Increase navigation with internal links and breadcrumbs.
The Foundation of SEO: Meta Tags and Their Impact
Title Tags: Title tags are crucial for search engine visibility and attracting users, acting as the first impression in search results. Descriptive, keyword-rich title tags help search engines grasp the page’s content and influence click-through rates by providing a clear page preview. Effective title tags can significantly boost web traffic and SEO performance.
Meta Descriptions: Meta descriptions, while not affecting rankings directly, play a key role in user engagement. These summaries under title tags in search results give a content snapshot, enticing users to visit the website. Including relevant keywords and a call to action can enhance their impact, making them vital for webpage optimization.
Robot Tags: Robot tags guide search engines in indexing and interacting with web pages. Using “noindex” and “nofollow,” owners can prevent indexing of specific pages or link following, managing SEO more effectively. These tags are key in avoiding duplicate content and focusing on SEO-beneficial content.
Social Media Tags: Optimizing for social media, especially with Open Graph for Facebook and Twitter Cards for Twitter, extends a webpage’s reach. Customizing how shared content appears on these platforms through titles, descriptions, and images can increase appeal and drive traffic. Effective use of social media tags boosts a site’s social presence and SEO strategy.
SEO HTML Best Practices for Optimal Website Performance
Enhancing Structure and Accessibility with Semantic HTML
Semantic HTML is crucial for SEO and web accessibility, structuring content with tags like <header>, <nav>, <article>, <section>, <aside>, and <footer> to make it meaningful and navigable. These elements improve accessibility by helping assistive technologies understand web page structure, enhancing the experience for users with disabilities. For SEO, semantic tags allow search engines to grasp the page layout and content hierarchy, aiding in accurate indexing and ranking. Using <nav> for navigation clarifies site structure, while <article> and <section> differentiate content areas, supporting better search engine understanding and performance.
Best Practices for Using Heading Tags
Heading tags should be used hierarchically for clear content structure, starting with <h1> for the main title down to <h6> for lesser headings, aiding search engines in understanding content importance. Incorporate keywords into headings to enhance SEO, ensuring they fit naturally. Maintain consistency in heading usage to keep content organized and logical, avoiding jumps in heading levels to preserve content flow.
Optimizing User Experience for Better SEO
Optimizing user experience boosts SEO by improving site rankings and engagement. Focus on:
Responsive Design
Responsive design, essential for a good user experience, adjusts content to fit various screens. The <meta name=”viewport”> tag ensures your site is viewable on all devices, which is crucial for adapting to Google’s mobile-first indexing.
Page Speed Optimization
Fast-loading sites enhance user satisfaction and are preferred by search engines. Optimizing code size, server response times, and browser caching are key. Tools like Google’s PageSpeed Insights offer actionable tips for improvement.
Image Optimization
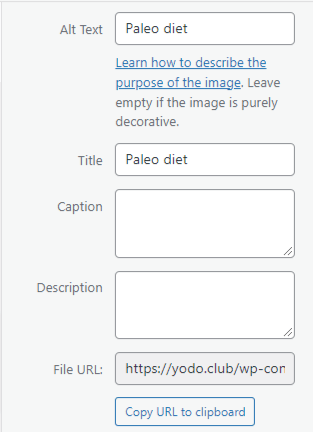
Optimized images reduce load times and improve user experience without sacrificing quality. Descriptive alt text for images aids SEO and accessibility, making content understandable for search engines and users alike. Various tools and plugins facilitate image optimization.
These practices enhance site usability and SEO, improving search rankings and user engagement.
Advanced SEO Techniques with HTML
Structured Data and Schema.org: Implementing Schema.org’s structured data enhances search results with rich snippets, displaying key information like pricing and reviews, thereby increasing the attractiveness and informativeness of listings. Schema.org supports various content types, improving SERP visibility and user engagement by providing context and promoting clearer search result presentations.
Canonical Tags: Canonical tags resolve duplicate content issues by indicating the preferred version of a page to search engines, preserving link equity, and clarifying ranking signals. This signal is crucial for sites with similar content across multiple URLs.
HTTPS for Security: Adopting HTTPS secures user data and serves as a search ranking signal. Secure sites are prioritized in rankings, underscoring the importance of HTTPS for SEO and user trust.
Internal Linking and Navigation
Effective internal linking optimizes SEO by spreading page authority and improving site navigation, aiding content discovery for users and search engines.
Strategies for Effective Internal Linking
-
- Anchor Text: Use clear, relevant anchor text for internal links to signal the linked page’s content.
- Content Hierarchy: Organize content hierarchically, linking frequently to high-priority pages to enhance their authority.
- Contextual Linking: Place internal links within relevant content to engage users and lead them to related information.
- Link to Deep Pages: Distribute links to deep internal pages, not just top-level pages, to spread authority site-wide.
- Limit Number of Links: Maintain a reasonable number of links per page to preserve link value and user focus.
The Role of Breadcrumb Navigation
Breadcrumb navigation enhances site usability by showing users their location within the site’s hierarchy and offering easy navigation to parent pages.
It benefits user experience and SEO by:
-
- Improved Navigation: Breadcrumbs clarify the user’s position on the site, enabling easy navigation to broader categories.
- Reduced Bounce Rate: By facilitating access to related content, breadcrumbs can lower bounce rates and boost content engagement.
- Enhanced SERPs Appearance: Breadcrumbs can appear in Google’s search results, making listings more appealing and potentially increasing click-through rates.
- Context for Search Engines: They provide search engines with insights into the site’s structure, supporting more effective content indexing.
Continuous Improvement and SEO Monitoring
Regular Content Updates
Frequent content updates boost SEO by signaling to search engines that your website is current and authoritative, aligning with the latest trends and information.
Such updates indicate website activity and proper maintenance, which can enhance indexing frequency, visibility, and keyword rankings.
Refreshing content can re-attract past visitors, fostering repeat engagement and increasing the chances of content sharing, thereby amplifying SEO impact.
Utilizing Analytical Tools
Google Analytics and Google Search Console are crucial for tracking SEO performance, offering insights into user interactions and page performance.
Google Analytics helps understand user behavior, such as how long they stay on your site and their navigation paths, informing content and structural enhancements.
Google Search Console provides:
-
- A search engine perspective.
- Identifying crawl issues and how content is presented in search results.
- Aiding in technical SEO and content optimization.
- Regular analysis of these tools helps in spotting trends, adjusting to user behavior changes, and refining SEO strategies, ensuring ongoing optimization and improved search rankings.
Conclusion
Adopting key HTML best practices is crucial for SEO optimization. By implementing these strategies, you can boost your site’s search rankings and user engagement. Apply these best practices to enhance your website’s SEO performance and user experience.
Additionally, addressing technical aspects such as fixing common HTML markup errors can further enhance your site’s performance and search engine ranking.





























































 & Passion.
& Passion.